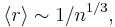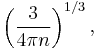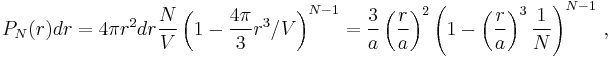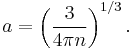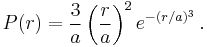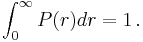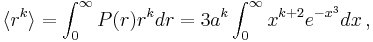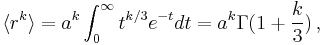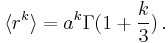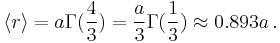Mean inter-particle distance
Mean inter-particle distance (or mean inter-particle separation) is the mean distance between microscopic particles (usually atoms or molecules) in a macroscopic body.
Contents |
Ambiguity
From the very general considerations, the mean inter-particle distance is proportional to the size of the per-particle volume 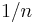 , i.e.,
, i.e.,
where 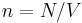 is the particle density. However, barring a few simple cases such as the ideal gas model, precise calculations of the proportionality factor are impossible analytically. Therefore, approximate expressions are often used. One such an estimation is the Wigner-Seitz radius
is the particle density. However, barring a few simple cases such as the ideal gas model, precise calculations of the proportionality factor are impossible analytically. Therefore, approximate expressions are often used. One such an estimation is the Wigner-Seitz radius
which corresponds to the radius of a sphere having per-particle volume 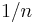 . Another popular definition is
. Another popular definition is
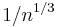 ,
,
corresponding to the length of the edge of the cube with the per-particle volume 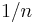 . Evidently, the two definitions differ by a factor of
. Evidently, the two definitions differ by a factor of 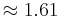 , thus one has to exercise care if an article fails to define the parameter exactly. On the other hand, it is often used in qualitative statements where such a numeric factor is either irrelevant or plays an insignificant role, e.g.,
, thus one has to exercise care if an article fails to define the parameter exactly. On the other hand, it is often used in qualitative statements where such a numeric factor is either irrelevant or plays an insignificant role, e.g.,
- "a potential energy ... is proportional to some power n of the inter-particle distance r" (Virial theorem)
- "the inter-particle distance is much larger than the thermal de Broglie wavelength" (Kinetic theory)
Ideal gas
Nearest neighbor distribution
We want to calculate probability distribution function of distance to the nearest neighbor (NN) particle. (The problem was first considered by Paul Hertz;[1] for a modern derivation see, e.g.,.[2]) Let us assume 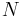 particles inside a sphere having volume
particles inside a sphere having volume 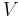 , so that
, so that 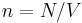 . Note that since the particles in the ideal gas are non-interacting, the probability to find a particle at a certain distance from another particle is the same as probability to find a particle at the same distance from any other point; we shall use the center of the sphere.
. Note that since the particles in the ideal gas are non-interacting, the probability to find a particle at a certain distance from another particle is the same as probability to find a particle at the same distance from any other point; we shall use the center of the sphere.
An NN particle at distance 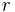 means exactly one of the
means exactly one of the 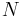 particles resides at that distance while the rest
particles resides at that distance while the rest 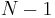 particles are at larger distances, i.e., they are somewhere outside the sphere with radius
particles are at larger distances, i.e., they are somewhere outside the sphere with radius 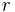 .
.
The probability to find a particle at the distance from the origin between 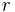 and
and 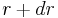 is
is 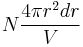 , while the probability to find a particle outside that sphere is
, while the probability to find a particle outside that sphere is 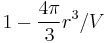 . The sought-for expression is then
. The sought-for expression is then
where we substituted
Finally, taking the 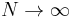 limit and using
limit and using 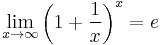 , we obtain
, we obtain
One can immediately check that
The distribution peaks at 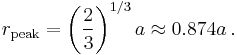
Mean distance and higher NN distribution moments
or, using the 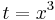 substitution,
substitution,
where 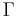 is the gamma function. Thus,
is the gamma function. Thus,
In particular,
References
- ^ Hertz, Paul (1909). "Über den gegenseitigen durchschnittlichen Abstand von Punkten, die mit bekannter mittlerer Dichte im Raume angeordnet sind". Mathematische Annalen 67 (3): 387–398. doi:10.1007/BF01450410. ISSN 0025-5831. http://www.springerlink.com/content/q133104qq7596l37/. Retrieved 2011-03-03.
- ^ Chandrasekhar, S. (1943-01-01). "Stochastic Problems in Physics and Astronomy". Reviews of Modern Physics 15 (1): 1. Bibcode 1943RvMP...15....1C. doi:10.1103/RevModPhys.15.1. http://link.aps.org/doi/10.1103/RevModPhys.15.1. Retrieved 2011-03-01.